The continuous development and integration of mobile devices brings simplicity and efficiency to many companies’ workplaces. However, these devices also carry numerous serious security risks, especially when used by medical institutions and their employees, in which case PHI exposure is possible. Mobile security is an extremely important topic that everyone needs to be familiar with nowadays.
This study done by Spyglass Consulting in the early 2015 showed that as many as 96% of the interviewed physicians used smartphones as their primary device to support clinical communications. These mobile devices were prefered because “they are easier to use and provide more enhanced functionality than outdated communication options provided by hospital IT including pagers, overhead paging systems, landline phones and fax machines.”
While data provided by Statista indicates a smaller percentage for the same indicator, the general trend here is rather obvious. More and more physicians use smartphones for professional purposes, and it’s very unlikely that this trend is going change.
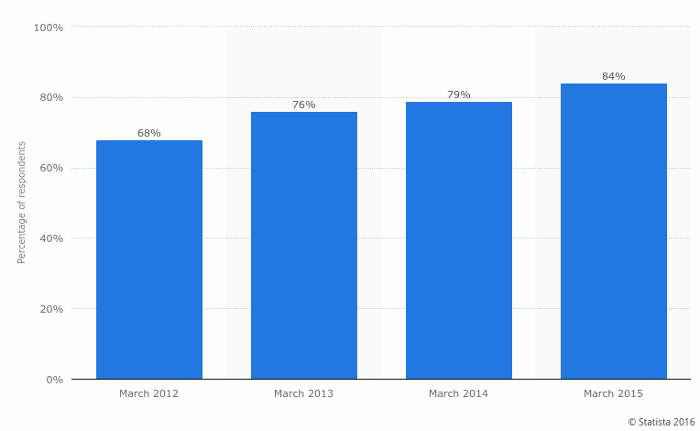
The employees are sure happy to use their mobile devices, but are healthcare organizations aware of the risks they are exposed to? Are they taking sufficient measures to minimize them? A recent study showed that as many as 82% of hospitals that were surveyed expressed grave concerns in regards to their ability to support and protect mobile devices, PHI, and the hospital’s overall IT infrastructure as a result of the constantly growing threat of cybersecurity attacks.

The conclusion that we can draw from all of this is rather pessimistic. Mobile devices carry great security risks, they are used practically universally by the staff, and organizations are having a hard time protecting these devices from potential security threats.
This sure sounds troublesome. The good news is that there’s a lot that you can do to protect your data, and we hope this article will help you in this uneasy task!
We’ll start by covering the most prominent security risks that mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets carry. We then show various examples of how these devices can be attacked and how sensitive information can be stolen from them. We also discuss the measures that you can take to ensure HIPAA compliance and to minimize the possibility of security breaches.
Ready? Grab a drink and let’s get started.
It’s a fact that mobile devices aren’t as secure as desktop computers or laptops, for which there are numerous security measures available that can be easily employed. Unfortunately, many of these efficient measures are simply unavailable for mobile devices. When an organization provides its own computers to their personnel for professional use, they normally come with sufficient protective measures and are therefore prepared to tackle various sorts of security threats that might arise. We certainly cannot be so sure about personnel’s own devices. These may not even be protected with technology like firewalls, encryption, or antivirus software.
The following graphic provided by HIPAA Journal demonstrates just how bad the situation with mobile devices is. You can see that over 100 million healthcare records were exposed in only half-a-year.
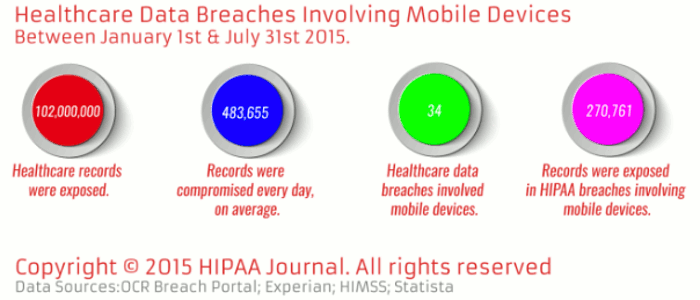
That’s certainly way too much sensitive information exposed due to insecure mobile devices, isn’t it?
All right, it’s very clear that mobile devices carry great risks and may lead to data breaches quite often, but how exactly does that happen?
We can separate the main attack and threat vectors for mobile devices into the following categories.
We all love our mobile devices for being so small and lightweight. This obviously nice characteristic may also turn out to be quite deadly. Mobile devices are easily stolen or forgotten in public places such as restaurants, taxis (190000 mobile phones are lost each year in London), or buses. This means serious trouble for us in most cases, unless the person who’d find the device does not try to do anything funny with it. If a malicious individual gains physical access to the device, no antivirus or firewall software will save it. “But what about screen lock?” - you ask. We have bad news for you here. Bypassing a screen lock protected with a simple passcode is not a very difficult task for someone with the right experience. While it certainly might fend off the attackers in some cases, the most persistent individuals won’t be swayed that easily.
Well, that’s bad enough. But what if all data on the stolen device is encrypted? No joy here either! Even if you carefully encrypt all the sensitive data that resides on your smartphone, it still can be accessed by using the right tools. Even if you did not have any sensitive data stored on the device at the moment of loss, but used to have it at some point in the past, you are still not 100% safe. Publicly available forensic data retrieval software allows to recover long-deleted data, even from a device that has been reset !
Obviously, a stolen or lost device means imminent trouble, but we don’t even need to go that far.
What about a simple and quite common scenario of doctors and other employees letting their kids play with their smartphones? Or leaving their devices unattended in presence of other people while they are away from their offices? Chances are you have already done one of these. Think twice the next time you leave your device unsupervised! Sensitive information is at risk in this case, since a simple press of a button might lead to a leak and technically, to a HIPAA violation.
So, what can we do to avoid all of this nasty stuff from happening to us?
Of course, the best possible solution for these problems would be for the organization to forbid their personnel to bring their own mobile devices, but that would certainly make people angry. What less drastic measures can be taken in order to allow the “Bring Your Own Device” strategy but still maintain a high security standard and HIPAA compliance? To give you a general idea of the general situation around BYOB in the enterprise world, this infographic does a good job.
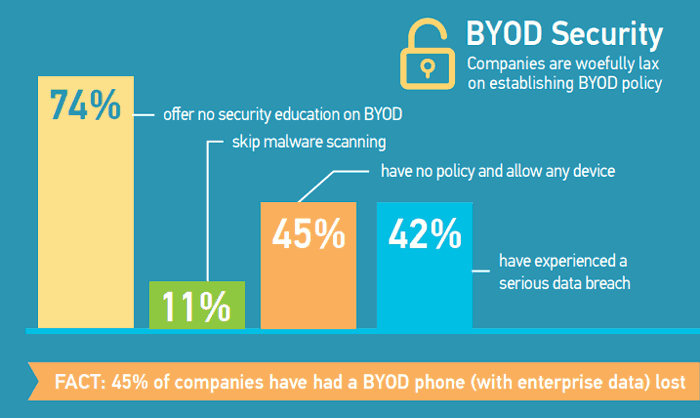
As you can see, there’s still a lot of work to be done here.
Protecting and securing sensitive information is the organization’s responsibility and it must make sure that all the sensitive information stored in its network is secure and protected. To address these concerns, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides the following mobile guidelines for organizations’ security officers and providers.
Here’s a summary of the most important things to consider from the NIST suggestions to tackle the issues we’ve discussed above:
All right! We’ve seen how we can ensure the basic physical safety of mobile devices. But our problems only begin here, since there are many more ways to gain unauthorized access to these devices without physically getting ahold of it! Let’s describe some of them.
Smartphones connected to a Wi-Fi network are no different from other such devices, and therefore are susceptible to the same types of attacks. The technology and applications made to hack into wireless networks are publicly available in the Internet, therefore a savvy enough enthusiast does not even need to be a top-rate hacker in order to hack into Wi-Fi devices.
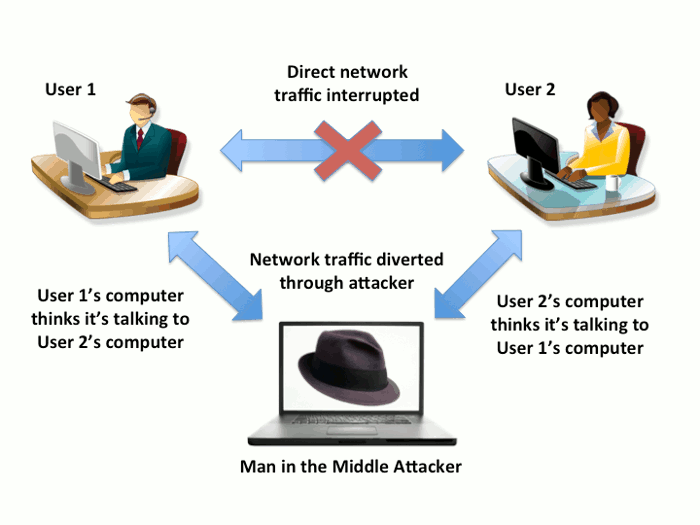
The man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack is especially popular and easy to perform. It is an attack where the attacker relays and possibly alters the communication between two parties who believe they are directly communicating with each other.
Cellular data transmission can also be intercepted and decrypted, and there are various devices available out there that were created just for that. The Stingray / GSM interceptor / IMSI catcher is equipment that can intercept cellular data from hundreds of phones over targeted areas.
Of course, hackers are more than happy to use these techniques and devices to exploit Wi-Fi and cellular data networks in order to steal sensitive and important information. A successful attack of such type would allow the attacker to access the victim’s webmail and authentication information for various online services used by the victim. For companies and institutions that use Wi-Fi hotspot services, the risks are extremely high, since Wi-Fi-connected mobile devices that are used to log in to the institution's internal system might give the attacker access to the database with tons of sensitive data. Needless to say, such a data leak would be catastrophic for any organization.
Okay, it’s really scary to think that someone might be intercepting sensitive information so easily without anyone noticing. Now that you’re aware of it, let’s refer to a couple of other NIST suggestions that will certainly help you to avoid the issues we’ve just discussed:
All right! That should keep us secure and rest assured there’s no one spying on us!
Now we are ready to move forward to yet another big threat―malicious code!
A great number of non-physical attacks can be directed at mobile devices, and these are constantly on the rise.
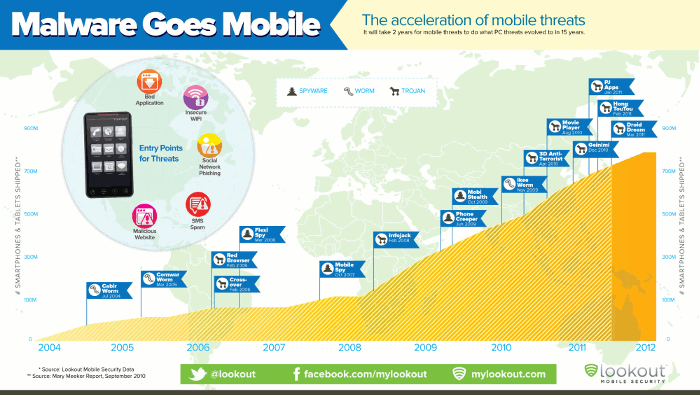
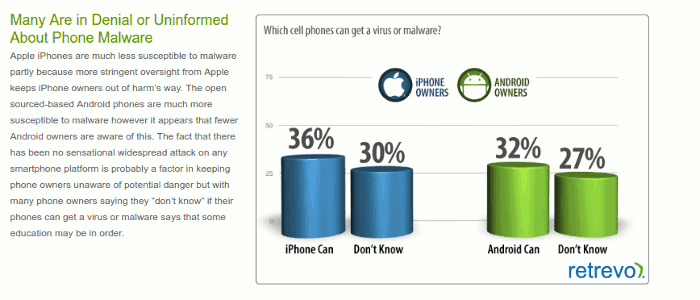
Malware, spyware, and other types of malicious code are a great danger to mobile devices, much higher when compared to personal computers. Yet, according to a survey done by a shopping website Retrevo, around one third of smartphone owners even realize their devices can be infected with malware, and another third do nothing to protect data on their phones. These two factors should immediately raise the red flags when taken into consideration together.
How exactly do these malicious applications attack mobile devices?
Malware is able to engage in a variety of sneaky acts―obviously without the user’s permission. For example, text messaging a premium rate number (and thus making your bill grow tenfold), sending your phonebook contacts spam or other unwanted information, and other malicious attacks of these sorts.
Spyware, on the other hand, can be used to steal important information, such as contact lists, call logs, SMS and MMS messages, GPS location, and browser history. Malicious applications that are capable of secretly recording and redirecting phone conversations and text messages to the attacker exist, and are being developed as you are reading this article. Generally, any type of sensitive information can be stolen and sent back to the attacker, be it online banking’s authentication information, credit card information, or PHI.
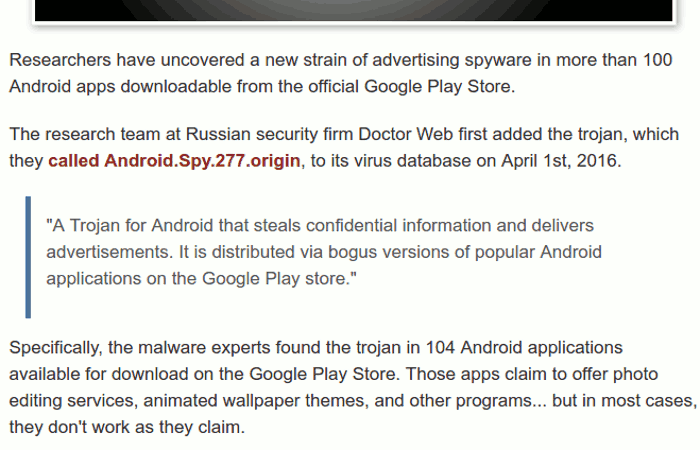
Here you can read an analysis done by Lookout of such spyware that was hiding in a legitimate application.

Most of the time, these malicious application are hidden in popular, legitimate apps normally found in the app stores of mobile phones. This way to spread malware is more commonly seen in Android app stores, but it has been seen in iPhones, as well.
In order to avoid all of this nasty stuff from happening, or at least to reduce the changes to fall victim to it, NIST recommends that all mobile device users should follow the basic mobile security practices:
Now that we’ve discussed different types of risks and how to tackle them, let’s also note how important it is to provide adequate training to employees to ensure data safety.
Since employee negligence is the leading cause of healthcare data breaches, the importance of frequent employee training cannot be understated. All HIPAA compliant institutions should offer their employees regular training sessions with the latest information on security and data privacy topics. Risk-aware employees are less likely to compromise organization’s security due to unsafe use of mobile devices. Increased investment in employee training can reduce the risk of a cyber attack by 45 to 70 percent, according to a 2015 study by Wombat Security Technologies and the Aberdeen Group. That’s obviously a smart thing to consider spending some of your budget on, since recovering from a cyber attack might cost many thousands of dollars!

Any organization employing the “Bring Your Own Device” strategy must ensure that their employees follow the basic mobile security practice and follow the guidelines provided in the previous sections as much as possible. Regular policy training and enforcement is an important part of HIPAA mobile security and helps your employees remember organizational guidelines.
This article covered the most important security risks that mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets are exposed to. We have showed various examples of how these devices can be attacked and how sensitive information can be stolen from them. We have also discussed the measures that everyone can take in order to ensure HIPAA compliance, and to minimize the possibility of security breaches and the resulting exposure of sensitive information.
Get some free help! Check out our free 42-Point Checklist for ways to make your practice HIPAA compliant.
Have questions or feedback? Please share them in the comments below.
Like this article? Share it!
